The chain of survival refers to a series of actions that, properly executed, reduce the mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest. Like any chain, the chain of survival is only as strong as its weakest link.
The chain of survival is an internationally recognised process. If each link in the chain is completed to a high standard, the patient has the greatest chance of survival.
What is SCA?
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) is when the heart rhythm becomes chaotic. It usually results from a disturbance in your heart that disrupts its pumping action, stopping the blood flow to your brain and the rest of your body.
It’s a medical emergency that if not treated immediately, will result in death within a few minutes.
-
Worldwide, seven million people are impacted annually.
-
More than 25000 per year in Australia suffer From SCA out of hospital every year. (Heart Foundation).
-
Every minute that passes without defibrillation reduced survival rate by 10%.
-
The average response time for emergency services is around eight to ten minutes.
-
Only 12% of people currently survive SCA.
-
Only 12% of SCA cases have a defibrillator available.
The Chain of Survival

1. Early Access
Recognising an impending cardiac arrest and calling for medical help immediately. Taking a first aid course can help you identify symptoms of SCA, enabling you to respond quickly.
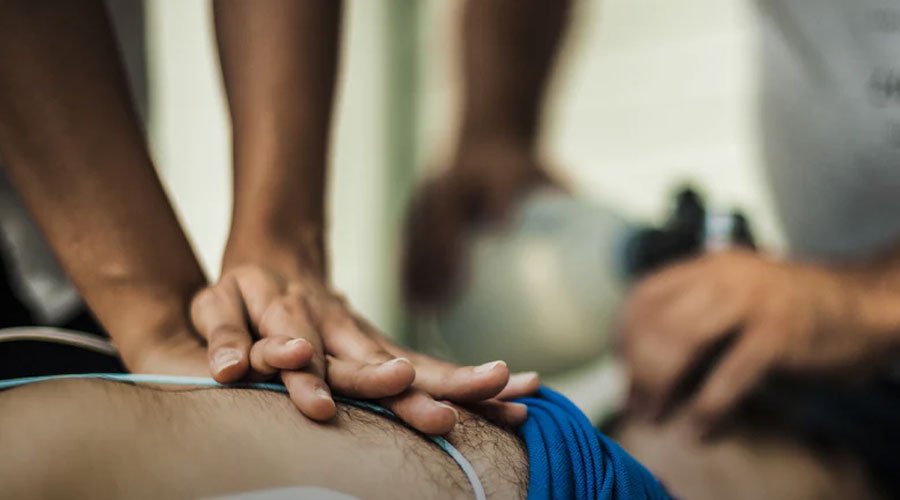
2. Early CPR
Provide CPR immediately after a patient collapses. CPR stands for cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It is a lifesaving procedure that is given to someone who is unresponsive and not breathing normally.
3. Early Defibrillation
Early defibrillation is the link in the chain most likely to improve survival. Public access defibrillation may be the key to improving survival rates in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, but is of the greatest value when the other links in the chain do not fail. Every minute that passes without defibrillation reduced survival rate by 10%.
FastAid support AEDs (automated external defibrillators) which contribute to more than one link in the chain of survival.
4. Early Advanced Care
Early advanced cardiac life support by paramedics is another critical link in the chain of survival. Medical treatment such as giving medication and stabilising the airway will increase the chance of survival even further.